PCT Ontology Modelling
This document is about Permissive Commons Technology - Ontology Modelling. The high-level introductory description of what ontologies and ontology modelling is about, has been moved to the page about UnderstandingOntologies.
In-order for CognitiveAI systems to meaningfully support the notion of 'common sense', semantic web related ontology technology is sought to be advanced. In-turn, the objective is to seek to address a number of underlying issues that are considered to be problems with it.
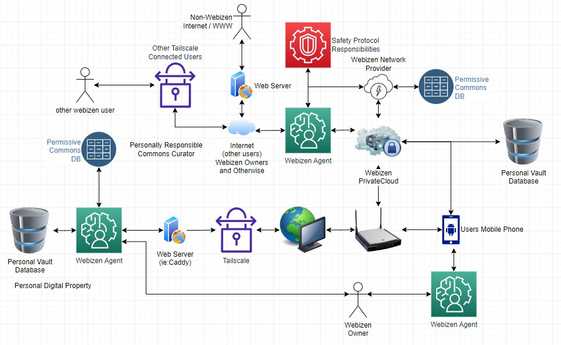
Webizen Diagram: A Basic UseCase Illustration
The above diagram was produced as part of the process of seeking to get some sort of grasp on how to address the GuardianshipRelations problems. Part of the purpose of the illustration, is to denote the difference between a persons 'private and personal' inforg (seeAlso: [[TheSemanticInforg&TheHumanCentricWeb — RealityCheckTech]]) and the resources that are electronically supplied as a consequence of social involvement with others.
This is intended to be empowered via [[WebScience/PeaceInfrastructureProject/SafetyProtocols/ValuesCredentials]] which in-turn require core ontologies; that are sought to be delivered using the PCT ecosystems.
Thereafter; the effect of these components, are intended to support the private operation of 'Webizen' (Agents).
NOTE: the end-concept of a 'webizen', is that it is a distinguishable class of robot, that is owned by an entity who is responsible for how it is made to operate; and that, all human beings using them, must first have their own. This in-turn acts to support, HumanCentricDigitalIdentity, [[WebScience/PeaceInfrastructureProject/SafetyProtocols/HumanCentricAI]] via tooling, that will include a HumanCentricOntology structure - that can be further improved upon overtime
The objective for now, is to define the requirements to establish a functional Webizen ecosystem that is then able to be used to further progress the works, upon a common set of principals and technology that supports those socio-economic and technological foundations
Problem Statement
HTTP(s) Ontologies are published online using a HTTP server and ICANN DNS.
PROBLEM 1: Often these resources disappear and may only later be found by searching for a record of it in archive.org or on github.
PROBLEM 2: The documents (and embedded semantics) may change without notice; and without a known mechanism to distinguish between the intended semantic meanings when defining the document vs. the future definitions that are engendered as a consequence of the content of an ontological dependency changing.
PROBLEM 3: The level of know-how relating to the production of ontologies can often lead to unintended meanings being semantically defined.
PROBLEM 4: Tools are most-often defined to be built around OWL which has a top-level concept of 'thing' and not everything relating to our conscious experience of life, is about things; nor are all entities things.
PROBLEM 5: In-order to decentralise and empower human kind, there must be a way to decentralise AI. There are various complex reasons, implications and consequences; and whilst these sorts of ideologies may not be universally sought, for those who do want to ensure a means for tooling to support the needs of themselves and others as human beings in a way that requires Decentralised (Human Centric) AI - decentralising ontologies (and other assets) in a manner that can (with the use of cryptography alongside other patterns) provide a fit-for-purpose capacities to participatorily create, make use of and rely upon electronic resources - is essential for all persons who exist in socio-economic structures that are managed using electronic systems.
As far as i am aware, there are not presently well-defined or well-known solutions that are 'fit for purpose' in relation to the requirements of the webizen project; The technical challenges include,
Defining a way to create ontologies (documents) that are referencable; and, a. 'tamper evident' b. temporally distinguishable. c. Able to be targeted as a specific version or group; with logic support for different usecases.
Defining cryptography methods 'ecosystem' that support the various usecases. (permissions, provonance, etc.)
Support inferencing methods for 'common sense' related functions; including, a means to process and formulate appropriate responses if the derivative of a functional request renders a result that is 'unclear' (ie: not binary - Yes/No)
Social Factors;
a. Provide explainability of decision making processes; including, via the use of permission systems that may distinguish the rights of access to resources based upon external factors (ie: a victim / perpetrator making claims, vs. the capacities of a judge/jury in a court of law)
b. Support for Children (ie: Content classifications)
c. Support for storing and maintaining access to the information created by persons who have become deceased.
d. Self-Archiving related methodologies; ideally, 'useful content' should never dissapear entirely; unless it becomes the case that no human being on the planet (voluntarily) wants to store it; or that it relates to some other complex use-case involving dignity (even then, perhaps the information should be stored somewhere as evidence, idk. perhaps laws?)
e. Support for basic economic considerations to be built into the protocols: This is not about the commercial abuse of a payments system, rather, it is about seeking to ensure that there is a caculation done on the biosphere and socio-sphere implications, as to provide protocol level evidence of such things as energy use and a means to abolish the support that is presently wide-spread witth respect to issues such as digital slavery.
Design Implications
Somehow there needs to be;
- A foundational ontology that defines requirements for a data-structure.
- A methodology that is able to be deployed over multiple [[Non-HTTP(s)Protocols]]
Broader Considerations
DNS: it is entirely possible that part of the solution may be to advance solutions that provide an update to DNS. If this is the case, the solution would need to work Side-By-Side with existing DNS.
SocioEconomics: There are material costs and gains associated with every human being, irraspective of age or competency. Existing systems have defines means to extract economic value in relation to any human entity; but they have not well defined how to ensure every human entity is also entitled to be a beneficiary; and indeed also, how that might work.
The GuardianshipRelations document provides some initial texts in relation to this topic.
PCT Ontology Modelling Requirements
[[TheValuesProject]] seeks to employ various pre-existing well-known instruments; such as those that have been created via the United Nations and various other internationally well regarded groups and institutions, that are not presently available in an [[SemanticWeb]] based format. Some information about existing [[Ontologies]] is provided via that link (although, not exhaustively).
In-order to support the SafetyProtocols and related ecosystems, some core work on the ontology methods is required; which will in-turn lead to the development of an ecosystem method for SocioSphereOntologies and BiosphereOntologies to compliment existing systems that are well defined for owl:thing related requirements.
Additionally,
- well known ontologies such as FOAF are now fairly outdated;
- Most reasoning / ontologicial systems are very much centered aruond the use of OWL; which has a top-level predicate defining anything that employs it as a sub-classes of
owl:thing - Ontologies are currently designed to refer to HTTP-URIs. By employing [[Non-HTTP(s)Protocols]] a method to define how to support various PCT-Webizen-Notes is thereby invoked.
- A foundational structure needs to be defined to thereafter built upon; and some consideration is being made about what the most appropriate approach may well be.
Thereafter, once these considerations are better understood; then, there is an ability to create the ontological structures of those ontology documents, including references to other .wellknown ontologies and related intended inferencing models, can be better modelled.
PCT Ontology Modelling Method
Ground-Up ontological modelling ideas....
Atomic Ontologies
The concept of Atomic Ontologies - is about the idea of forming an ontological approach that describes one term; rather than an entire syntax. thereafter, a group of these atomic ontological resources could be used to define more comprehensive ontological structures.
Foundational Requirements: RDF Dictionaries?
In-order to address the semantic ontology problems, perhaps the best way is to define a new approach to forming the foundational ontology via a different sort of modelling technique.
An idea of how this may be achieved; is via the use of a dictionary as a sourcefile; for Generating a semantic dictionary using AI (NN/DL/ML); which may then act as a datasource for the creation of an app that provides support for modelling an ontological structure based upon those fundamental predicates.
This initial process, would likely not include an array of terms that relate to brands and various areas of science, yet, the same process could be undertaken with other dictionaries.
Thereby providing a means to create a mapping technique between the historical / traditional foundational predicates; and in-turn, the ability to generate more meaningful relationships with the meaning of other terms; and thereby provide an underlying context for producing ontological (knowledge) modelling.
Whilst i'm not sure if this theory has merit; i'm working to figure out how it might work now...
Part of the consideration is; whether and/or how these sorts of requirements might fit into an ecosystem that is designed to employ CognitiveAI related applied computer science theories and principles.
NowTherefore; a few questions with unknown answers.
Forming Trustworthy Ontological Structures
The existing Sematnic Web tooling, is built upon HTTP(s) Identifiers and as noted otherwise, there are an array of qualities that are considered to be issues.
Given the permissive commons ecosystem works provide a foundational opportunity to redefine how these sorts of things are implemented; in a new and different sort of way that may extend beyond merely ensuring support via protocols other than HTTP(s) and related version control and permissions related ecosystem characteristics.
I am now therefore working through some ideas that will remain largely undefined until the though processes are somewhat advanced (as a consequence of having done the work).
Discovery work
The content below is the discovery work that is being defined as it is written / produced, that is seeking to process a series of complex problems without a known answer or defined approach; as to catalogue related considerations in-order to create one (an approach)
How to best construct an artificial learning model that provides a coheasive data-set as to support a systematic method for foundational principals that can then in-turn be employed for producing SocioSphereOntologies, BiosphereOntologies and most importantly a HumanCentricOntology.
The first objective would be to describe a method that can be used to create a resource (software) that is able to be used with the english language.
(it goes without saying, that other languages should be supported - but i'm focusing firstly, upon the language i mostly use and best know)
QUESTION: is it better to start with the use of english or the use of mathematics; or is it best to ensure the use of both, in-order to create a bridge between human use of linquistics and the computational use of human language, in a way that's in-turn going to be used computationally.
English Language Concepts
A few core concepts;
- Sentence - a set of words that is complete in itself, typically containing a subject and predicate, conveying a statement, question, exclamation, or command, and consisting of a main clause and sometimes one or more subordinate clauses.
- word - a single distinct meaningful element of speech or writing, used with others (or sometimes alone) to form a sentence and typically shown with a space on either side when written or printed.
- morphemes - a meaningful morphological unit of a language that cannot be further divided (e.g. in, come, -ing, forming incoming ).
- Grammar - the whole system and structure of a language or of languages in general, usually taken as consisting of syntax and morphology (including inflections) and sometimes also phonology and semantics.
- meaning - what is meant by a word, text, concept, or action.
- known - recognized, familiar, or within the scope of knowledge.
- explained - make (an idea or situation) clear to someone by describing it in more detail or revealing relevant facts.
- antecedent - a thing that existed before or logically precedes another.
- consequent - following as a result or effect.
- Translation - the process of translating words or text from one language into another.
- sense - a faculty by which the body perceives an external stimulus; one of the faculties of sight, smell, hearing, taste, and touch.
- Common Sense - good sense and sound judgement in practical matters.
- Definition - a statement of the exact meaning of a word, especially in a dictionary.
NOTE: above definitions are generally provided in relation to the use of the term as a noun.
1. NOUN - A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea. 2. PRONOUN - A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. 3. VERB - A verb expresses action or being. 4. ADJECTIVE - An adjective modifies or describes a noun or pronoun. 5. ADVERB - An adverb modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. 6. PREPOSITION - A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence. 7. CONJUNCTION - A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses. 8. INTERJECTION - An interjection is a word used to express emotion.
One of the Antecedent to words is letters of an alphabet, which may in-turn be expressed in an array of computational codes - here's a tool that illustrates this.
Computational Language Concepts.
Whilst seeking to make the note, i also understand the fundamental nature of it; apologies,
Computers fundamentally 'speak' binary. Various abstrations are thereby created, which are fundamentally based upon mathematics.
There are various 'command' structures that relate to different computational models; relating both, to hardware and software based instruction-sets. The way through which this is performed has a significant impact on the amount of power (energy) and time (amount of processing required) to achieve some sort of derivative function. Higher level languages or abstractions (from a computing point of view) are able to engender results that other lower-level methodologies are able to achieve with less time (computational horsepower) / energy.
Computers are not manufactured to comprehend natural (human) language; although, it is increasingly 'done' via increasingly sophistocated systems, etc.
Consideration:
If a possible approach to generate a foundational ontology relating to the use of the english language is able to be produced (and consequentially via use / contributions, refined); is it better to start with the predicates relating to computational language concepts, or human (natural) language concepts? or, is a AI model defined to process a model that involves both?
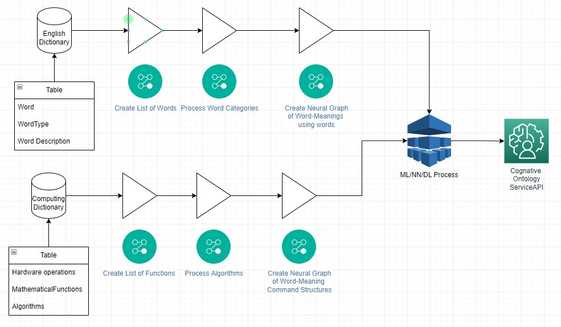
Whilst the diagram is most certainly flawed / incorrect (requires more work) the general gist of the concept that i'm working through is difficult to conceptually construct; so i hope this helps (even if / as it has errors) - noting in particular, the importance of [[PCT-Webizen-Notes/Webizen/EconomicSystems/Centricity]] factors...
Therein - the general idea or concept is; to process the english language via a AI Process (meaning DL, ML, NN, CNN, etc.) in a manner that can thereafter be used to define a tool (Software Program) for producing RDF based ontologically defined assets / code (documents).
The intended useful purpose of this program is to foundationally support the development of PCT Ontologies, which are in-turn a critical requirement for the production of PCT more broadly; including but not limited to, furnishing the means for others to form alternative and/or different foundational ontological schemas and related processes for logic mapping.
Processing Dimentionalities
- Time
- Energy
Both time and energy have complex attribution frameworks associated with the useful application of those concepts to different constituent 'ecosystems' processes.
- Correctness and implication of incorrectness
Methods to consider uncertainty.
- Centricity
Employing an Agent Centric Approach which employs the use of cryptography; whilst ensuring the operational use of it, is HumanCentric.